

Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a gentle and effective fertility treatment offered at Lotus IVF, the best IUI clinic in Bareilly, where dreams of motherhood are nurtured with care. This minimally invasive procedure places high-quality sperm directly into the uterus, bringing hope to couples facing challenges in conceiving.
The term "intrauterine" means "inside the uterus," symbolizing the journey of life itself. Under the compassionate care of Dr. Shruti Ghate, the best IUI doctor in Bareilly, every step is guided with expertise and understanding, bringing you closer to the joy of parenthood.
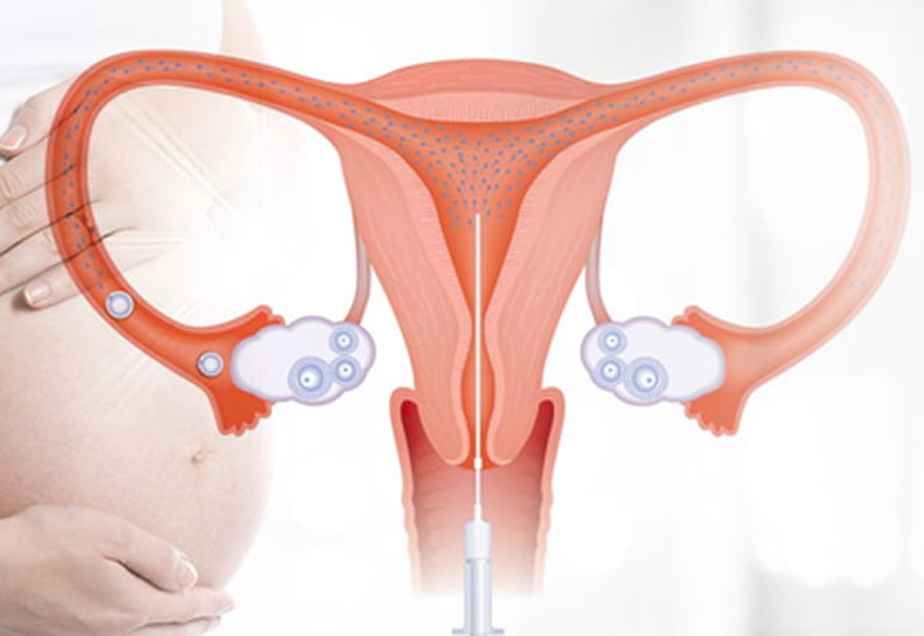
Couples recommended for IUI are required to go through a number of investigations and procedures:
Female partner is typically required to undergo fertility medication often oral medicines ,these medications aim at the growth of a single egg in the ovary.
The male partner is requested to provide a semen sample. To optimize the quality of semen sample, it is processed by different techniques such as swim up method and double density method to improve the quality of semen sample. The good active motile sperms are selectively chosen for insemination inside the uterus.
After the female partner has undergone ovulation , her doctor will perform an out patient procedure to directly place the sperm into her uterus.
IUI is often recommended for couples experiencing challenges in conceiving naturally due to infertility issues, hormonal imbalances, or other health factors. Additionally, it can be utilized by same-sex couples, single women, and individuals who have undergone a vasectomy. For couples who are not yet ready for IVF, IUI may present a more suitable option.
IUI treatment is generally regarded as safe, cost-effective, and can offer successful outcomes for couples facing conception difficulties. Before determining if IUI is appropriate, it's essential to discuss your options thoroughly with your doctor. With appropriate guidance and support, IUI can serve as an effective fertility solution, aiding couples in realizing their family-building aspirations.
The optimal timing for an intrauterine insemination (IUI) is usually during the woman's fertile period, which typically occurs between ovulation and the onset of menstruation. This timing can be identified using techniques like basal body temperature charting, ovulation predictor kits, or ultrasound monitoring. Consulting with a fertility expert is advisable to establish the most suitable timing for an IUI.
The likelihood of achieving pregnancy through intrauterine insemination (IUI) can vary based on several factors, including the woman's age, the underlying cause of infertility, and the number of IUI cycles attempted. Data from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine suggests that the success rate for IUI is approximately 10-20% per cycle for women under 35 years old. For women over 40, the success rate tends to be lower, around 5%. However, the chances of pregnancy with IUI can be improved by incorporating assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
The likelihood of complications with intrauterine insemination (IUI) is generally minimal. Common risks include cramping, bloating, and mild discomfort during the procedure. There is a slight chance of infection or bleeding. Multiple pregnancies may occur in rare instances. Overall, the risk of complications is typically low, and serious issues are uncommon. Nonetheless, it's essential to have a discussion with a healthcare provider about the potential risks and benefits before proceeding with IUI, as with any medical intervention.
Some women liken the sensation during intrauterine insemination (IUI) to that of a Pap smear, suggesting it can be painless. Any subsequent cramping may occur but could also be attributed to ovulation. Discomfort at the cervix is possible as well.
IUI typically carries minimal risks. Following the procedure, the female may encounter mild cramping, which usually subsides quickly, and/or temporary spotting.
The number of embryos transferred depends on various factors including age, embryo quality, and patient preference.